PDC Machines Argon Compressor
What is Argon?
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It belongs to the noble gas group on the periodic table, which also includes helium, neon, krypton, xenon, and radon. Argon is denser than air, and its density increases with decreasing temperature.
At room temperature, argon exists as a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas. Argon has a boiling point of -185.9°C (-302.6°F) and a melting point of -189.3°C (-308.7°F).
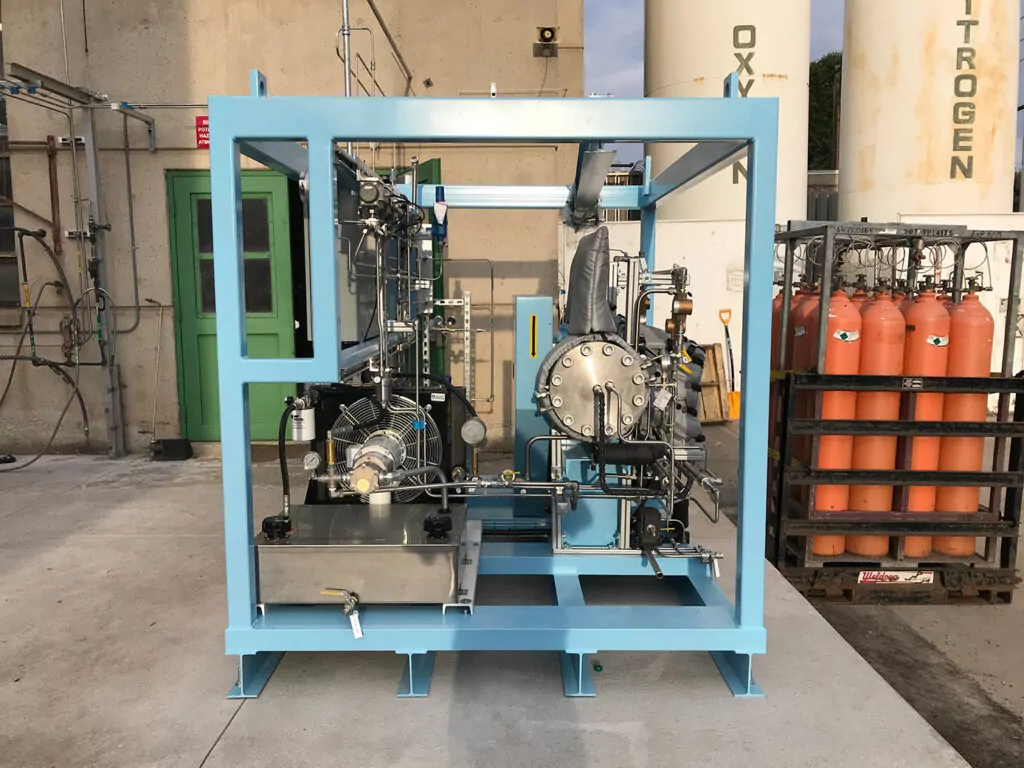
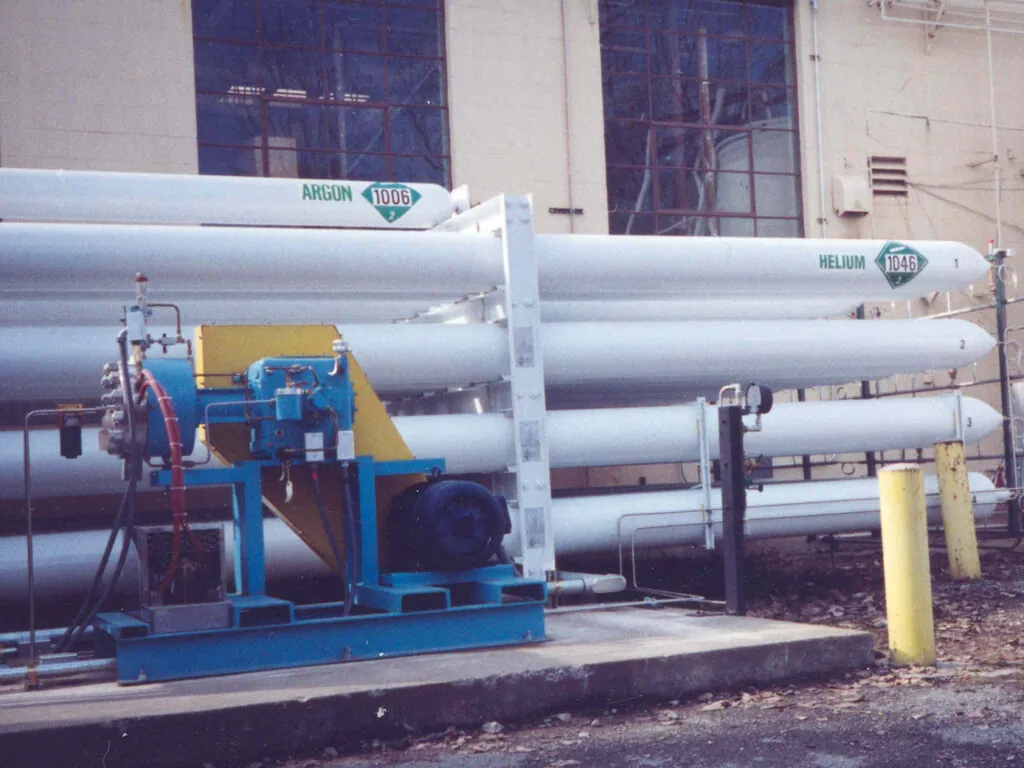


Applications of Argon:
Welding: Argon is widely used as a shielding gas in welding processes. It protects the weld area from atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen, preventing oxidation and ensuring high-quality welds.
Lighting: Argon is used in various types of lighting, including fluorescent lamps and neon signs. When an electric current is passed through argon gas, it emits a distinctive color, often blue or violet.
Laboratory and Scientific Applications: Argon is used in laboratories for its inert properties. It is often employed in gas chromatography and other analytical techniques where a non-reactive atmosphere is needed.
Electronics: In the manufacturing of semiconductors and other electronic components, argon is used as a process gas or in plasma technology.
Medical Applications: Argon is sometimes used in medical procedures. For example, argon laser therapy is employed in ophthalmology for eye surgeries.
Metallurgy: In the production of specialty metals such as titanium and zirconium, argon is used as a protective atmosphere during certain processes.
Food and Beverage Industry: In the food industry, argon can be used as a preservative gas to displace oxygen and extend the shelf life of certain products.
Geochronology: Argon-argon dating is a radiometric dating method used to determine the age of rocks and minerals. It relies on the radioactive decay of potassium-40 to argon-40.
Gas Atmosphere for Analytical Instruments: In analytical instruments like mass spectrometers and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrometers, argon is used as a carrier gas or in the sample environment.
The diverse range of applications stems from argon’s inert nature, which makes it suitable for processes and environments where chemical reactivity must be minimized.
Compressing Argon
Compressing argon involves increasing its pressure, typically for storage or industrial applications. Argon, like other gases, can be compressed using a compressor. Here’s a general overview of the process:
Compressor Selection
Use a compressor suitable for handling noble gases like argon. Diaphragm compressors or reciprocating compressors are often employed for this purpose.
The choice of an argon compressor depends on the required pressure, flow rate, and purity of the compressed argon.
Storage
The compressed argon is then stored in high-pressure cylinders or tank containers. These containers are designed to withstand the pressure and are often constructed with materials compatible with high-pressure gases.
Inlet Filtration
Before compression using diaphragm compressors, it’s essential to ensure that the incoming argon is clean and free of contaminants. Filtration systems are often used for this purpose.
Safety Considerations
Safety is a crucial aspect of working with compressed gases. Diaphragm compression systems should include pressure relief devices, and operators should be trained on safe handling procedures. Compressed gases, including argon, should be stored and handled in accordance with relevant safety regulations.
Compression Process
The diaphragm compressor takes in argon gas at a certain pressure and as a gas booster, compresses it to a higher pressure. The compression process increases the temperature of the gas. Depending on the system, there may be cooling stages to control the temperature.
Distribution
Compressed argon can be distributed through pipelines or in cylinders, depending on the specific application.
Cooling
Compression of argon generates heat, and excessive heat can be detrimental. Cooling systems are often incorporated to remove the heat generated during compression. This can involve intercoolers and aftercoolers.
Important Notes
Argon, being an inert gas, doesn’t react readily with other substances. However, safety measures are crucial, especially when working with compressed gases.
The choice of compression equipment and process parameters depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as the desired pressure and purity of the compressed argon.
Always follow industry guidelines, safety protocols, and manufacturer recommendations when working with compressed gases to ensure a safe and efficient process.
What is an Argon Gas Compressor? How Does it Work?
An a diaphragm type argon compressor is a mechanical device designed to increase the pressure of argon gas to a level suitable for various industrial applications. Argon gas compressors are available in a range of types and configurations, catering to different pressure requirements and application needs.
PDC Machines’ argon gas compressors are renowned for their reliability, efficiency, and precise control over the compression process. Advanced engineering and materials ensure that these compressors can handle the demanding requirements of various industrial applications, providing a continuous supply of high-purity argon gas or for cylinder filling applications.
By leveraging the latest technological advancements, PDC Machines’ argon compressors guarantee smooth operation, minimal maintenance, and optimum performance, making them an essential asset in numerous industries worldwide.
Why Argon Compressor Manufacturer PDC Machines?
Safety interlocks
PDC’s argon compressors are completely instrumented for safe and automatic operation.
Fast Acting Leak Detection System: Included with every PDC argon compressor is a leak detection system. This system detects diaphragm or seal failures. Our leak detection system monitors the gas and hydraulic sides of the compressor and will sound an alarm and/or shut down the compressor when it detects an anomaly or failure.
Leak-free argon compression: PDC’s compressors compress argon in an ultra-pure state. There is no contamination of the argon gas during compression.
Unique Oil Distribution System
PDC argon diaphragm compressors hydraulic systems are designed in such a way as to ensure uniform diaphragm deflection, prevent knocks, vibration, cavitation and yield smooth, and quiet compressor operation.
Fast Acting Leak Detection System
Included with every PDC argon compressor is a leak detection system. This system detects diaphragm or seal failures. Our leak detection system monitors the gas and hydraulic sides of the compressor and will sound an alarm and/or shut down the compressor when it detects an anomaly or failure.
Low Energy Costs
PDC’s argon compressors use a heavy flywheel to provide energy. In addition, Duplex and two-stage argon diaphragm compressors can be horizontally opposed to further reduce horsepower requirements and energy usage, resulting in ease of use and cost savings for the end user.
Leak-free argon compression
PDC’s compressors compress argon in an ultra-pure state. There is no contamination of the argon gas during compression.
International Standards Compliance
Argon compressor manufacturer PDC’s compressors can be designed and certified to comply with US and global international codes and standards.
High Compression Ratio
Our argon compressors can achieve typical compression ratios up to 10:1 for certain models.
Successful Organization
PDC Machines owes much of its success to building long-term relationships, with proven performance and complete customer satisfaction. We value our clients and demonstrate this in the way we work with them. We have earned a reputation for delivering the highest quality product on time and at competitive pricing.
Superior & Extended Diaphragm Compressor Life
All aspects of PDC’s argon gas compressors enhance component life, improve operability, and reduce and simplify maintenance.
Reliable Products
PDC Machines offers a broad selection of standard and custom-designed gas argon compressors with a comprehensive assortment of options.
PDC’s approach to engineering and manufacturing provides for cost effective product solutions that are high quality, high reliability and consistently perform under pressure.
Low Maintenance
PDC compressors typically only require routine oil changes for the lubrication system.
Customer Support
PDC Machines provides outstanding customer support for all our clients. Our compressors are backed by a veteran team of sales engineers, project engineers, factory service technicians, and a global support network to ensure maximum uptime of our customer’s operations.
Automatic Unloading System
PDC’s argon compressors are automatically re-primed at start-up. Manual start-up requires an experienced compressor technician to re-prime the argon compressor. Incorrect priming can cavitate the compressor and damage the heads, bolts, diaphragms, O-rings, process and hydraulic system. PDC’s argon diaphragm compressors avoid this potential issue with our cutting-edge re-priming tech.
Spare Parts Availability
PDC Machines stock a full selection of consumable parts including diaphragms, O-rings, process check valves, hydraulic check & oil regulating valves, tubing components, and more.
Quiet Operation
Below 85 dBA at 1 meter without sound-proofing enclosure.
Please Send Us Your Requirements
PDC offers compressors for argon and other gasses from basic to fully automated turnkey gas compression systems which include piping, instrumentation, and controls.
For More Information: